Measuring and Interpreting Blood Sugar Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Blood sugar levels play a critical role in our health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing this condition. Understanding how to accurately measure blood sugar levels and interpret the results is essential for managing one’s health effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the methods of measuring blood glucose, the significance of different levels, and how to ensure optimal management of blood sugar.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a crucial energy source for the body’s cells. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps cells absorb glucose. Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is vital since both high and low levels can lead to serious health issues.
What Constitutes Ideal Blood Sugar Levels?
According to Allopathic Medicine, blood sugar levels are categorized as follows:
- Normal fasting blood sugar: 70–99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L)
- Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L)
- Diabetes: ≥ 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L)
Methods of Measuring Blood Sugar Levels
There are several methods available to measure blood sugar levels, and selecting the appropriate method depends on the individual’s needs and circumstances. Below are the most common techniques:
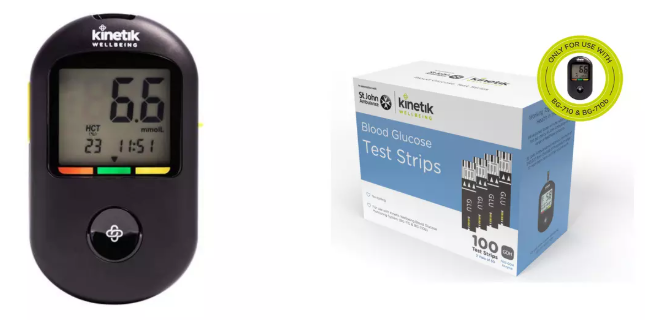
1. Home Glucose Meters
Home glucose meters are widely used for monitoring blood sugar levels. Users will typically:
- Wash their hands thoroughly.
- Prick their finger with a sterile lancet to obtain a blood drop.
- Place the blood drop on a test strip inserted into the glucose meter.
- Read the result displayed on the meter.
This method allows for frequent monitoring and is crucial for effective diabetes management.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs provide ongoing monitoring of blood sugar levels through a small sensor inserted under the skin. These devices measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid and communicate with a handheld receiver or smartphone app to display trends and levels.
Benefits of CGMs include:
- Real-time monitoring of glucose levels.
- Alerts for high and low blood sugar levels.
- Trend data to help analyse patterns.
3. Laboratory Testing
Healthcare providers may recommend laboratory tests to measure blood sugar levels more accurately. The common tests include:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): Measures blood glucose after fasting for at least 8 hours.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Assesses how the body processes glucose by measuring blood sugar before and after consuming a sweet drink.
- Haemoglobin A1c Test: Provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Levels
Understanding how to interpret blood sugar results is crucial for effective management of health. Here’s how to read the numbers:
Blood Sugar Level Interpretation
The values obtained from testing reflect various conditions:
- Hypoglycaemia: Levels below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) indicate low blood sugar, which can lead to symptoms like dizziness, sweating, and confusion.
- Hyperglycaemia: Levels above 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) after meals can indicate poor blood sugar control.
Long-Term Management
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is critical in reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Effective management strategies include:
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
- Adopting a balanced diet rich in fibre, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Taking prescribed medications as directed.
Conclusion
Measuring and interpreting blood sugar levels are essential practices for anyone interested in maintaining or improving their health, particularly those with diabetes. With the right tools and knowledge, individuals can effectively monitor their blood sugar, identify trends, and take proactive steps to manage their health. By understanding how these levels are measured and interpreted, people can pave the way for a healthier future and reduce the risks associated with abnormal blood glucose levels.
There you have it… See what works for you…
Campbell M Gold
To Create Health, Wealth, Success, and Longevity through the Power of Your Subconscious Mind, Visit: Campbell M Gold.com
Visit The Store and see what else can be of help